Asthma has an impact on the quality of life of over 11% of the adult Australian population and is a cause of much absenteeism and many hospital admissions.1 As most people with asthma are managed in primary care,2 it is necessary to develop an evidence-based approach to the structural, organisational and personal aspects of asthma management in the primary care setting that will foster improved care. In the past, a reactive model of asthma management prevailed, with most patients considering the need to consult a general practitioner only when they had symptoms.
In 2001, the Australian Government introduced a policy initiative that recompensed GPs for completing the Asthma 3+ Visit Plan, encouraging them to adopt a more proactive approach to asthma management.3 This model was implemented without an adequate evidence base,4 and analysis indicated a poor uptake by practices before the commencement of this study in 2004.5
Our study aimed to test the efficacy of a process of systematic care for adult patients with asthma that focused on an integrated model of using up-to-date registers of patients with asthma and proactively recalling patients for review. There is some evidence that applying many of the elements of this model to children improves their care and health outcomes.6
We conducted a pragmatic cluster randomised controlled trial over the 2 years 2004 and 2005 in urban and rural areas of South Australia and New South Wales. Because the focus was on systems within general practice rather than on treatment of individual patients, the general practice was the unit of randomisation.
Our hypotheses were that, for adults with moderate to severe asthma managed with systematic care, compared with those managed under usual care, there would be improvements in measures of:
clinical asthma outcomes (primary hypothesis 1);
the process and quality of care provided (primary hypothesis 2); and
acceptability to patients, health-related quality of life, and asthma self-management skills (secondary hypotheses).
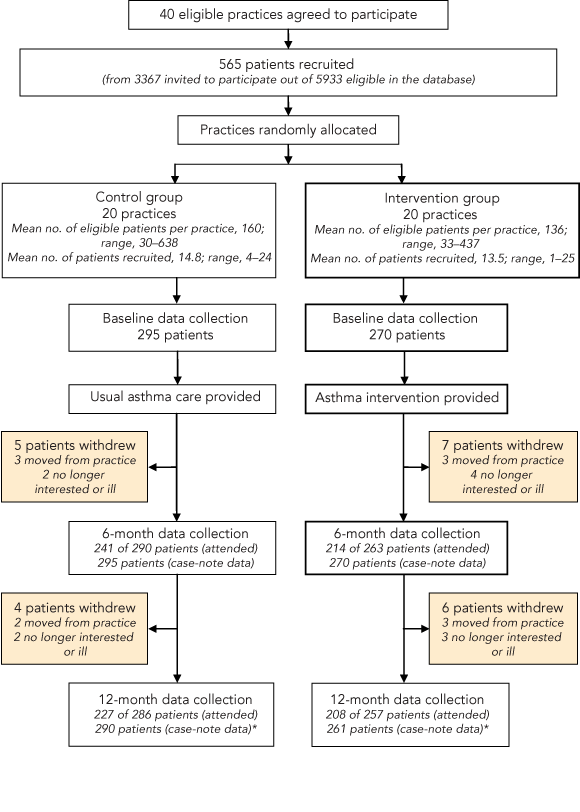
Letters of invitation were sent to 942 practices within 10 Divisions of General Practice. Practices needed to be computerised and to agree to allow research nurses to work from their premises and have access to patient case notes. Between 6 April and 19 October 2004, 40 practices — 26 urban and 14 rural — agreed to participate. Ten practices in each state were allocated to the intervention and control groups.
Patients were identified through the practice’s prescription database. Eligible patients had to be 18 years or older, taking inhaled corticosteroids and assessed by the GP as having either moderate or severe asthma based on the guidelines of the National Asthma Council of Australia.7 Exclusion criteria included a diagnosis of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease only, inability to read and/or understand English, significant cognitive impairment and other severe illnesses likely to affect participation.
From the 5933 patients identified as potentially eligible, a letter was sent to 3367 inviting them to participate. In practices with fewer than 100 eligible patients, all patients were invited; for those with more than 100, a random selection of 100 eligible patients were approached. A total of 565 patients provided written informed consent and were enrolled between 8 June and 22 December 2004 (response rate, 16.8%) — 323 in SA and 242 in NSW. The mean number of patients per practice was 14 (range, 1–25).
The asthma management intervention comprised:
assistance in setting up a register of patients with moderate or severe asthma;
assistance in implementing a recall system, including the use of a postcard prompt;
education of GPs and practice nurses about systematic asthma care (written information) and the use of spirometry (training workshops);
education of staff about their role in systematic care and claiming the Asthma 3+ Visit Plan incentive payment (written information and one-on-one discussions); and
provision of feedback by sending a summary of selected baseline data to GPs, with a reminder of what constituted best-practice care.
The central element was the posting of a yellow postcard to all participating patients in the intervention practices, outlining the benefits of asthma review and inviting them to attend their practice specifically for that purpose. This postcard was sent 2 months after patient recruitment. If there was no response to the postcard, one follow-up phone call was made by practice staff.
Control group practices continued to provide usual care for their asthma patients.
Clinical asthma outcomes were collected through a patient questionnaire at baseline, 6 months and 12 months. Lung function was measured by spirometry performed by the research nurses.
Measures of the process of care, based on asthma guidelines, were collected from review of patient case notes.
Acceptability to patients was measured by the number of patients who attended for review (from the case notes) and a patient questionnaire.
Patients’ health-related quality of life was measured at baseline, 6 months and 12 months using the Mini Asthma Quality of Life Questionnaire.8
Asthma self-management skills were assessed at baseline, 6 months and 12 months using a questionnaire assessing attitudes and beliefs about asthma9 and asthma self-management skills scenarios10 (presented verbally, with scoring of responses based on a 1996 report11 updated to current guidelines).
To ensure quality of data collection, all of the research nurses were trained in use of the EasyOne spirometer (ndd Medical Technologies, Zurich, Switzerland) by the same expert, and were provided with a written protocol and monitored by the project manager. The two nurses who reviewed the case notes were trained by the project manager and followed a written protocol. Comparison of a sample of 15 case-note reviews showed an acceptable level of agreement (κ ranging from 0.63 to 0.81).
Box 1 shows the recruitment of practices and patients, and the retention of patients through the trial.
There were no differences between the 20 intervention and 20 control group practices in terms of size, socioeconomic index, or organisational structure. Only six control group and four intervention group practices had existing asthma registers, with one control and two intervention group practices previously running asthma clinics. There were 96 consenting GPs, of whom 74 (77%) were male; their mean age was 48.3 years, and there were no significant differences in the characteristics of control group and intervention group practice GPs.
Box 2 outlines the demographic and asthma characteristics of patients in the control (295 patients) and intervention (270 patients) groups, as well as a comparison with non-participants (eligible patients who were either not approached or who declined to participate). Overall, participants were older than non-participants, and were more likely to be female and to live in lower socioeconomic areas.
The intervention group had a slightly higher proportion of women compared with the control group, had lower socioeconomic status and were less likely to be employed.
Primary hypothesis 1: Box 3 shows the variables used to assess patient clinical outcomes, with asthma on waking at least weekly in the previous 4 weeks as the primary endpoint. There were no statistically significant differences between the groups for any variables at 12 months.
Primary hypothesis 2: In terms of the process and quality of care, Box 4 shows that provision or review of a written asthma action plan in the previous 6 months (primary endpoint) was significantly greater in the intervention group.
Secondary hypothesis — acceptability to patients: Almost half the patients (46%) responded to the postcards by making an appointment for an asthma review, but only 32% actually attended and used the appointment for that purpose (Box 5). Patients’ rating of their satisfaction with asthma care from both the GP and the practice as a whole revealed no statistically significant differences between the two groups.
Secondary hypothesis — quality of life: Scores from the quality-of-life questionnaire showed no statistically significant differences between the two groups at 12 months, either for the individual domains or the total score.
Secondary hypothesis — asthma self-management skills: There were no statistically significant differences at 12 months in intervention group patients’ knowledge about asthma or their ability to apply that to hypothetical asthma attack scenarios, compared with control group patients.
Our trial of systematic asthma management resulted in a statistically significant difference in the rate of provision of a written asthma action plan by treating GPs, but not in other aspects of the process of care, quality of life, health outcomes or patient satisfaction. Written asthma action plans have been shown to improve the care of patients,12 and it is disappointing that there was still only a small proportion of patients receiving them.
Our results overall do not accord with a previous systematic review that found that a model of care incorporating self-monitoring, regular medical review and a written action plan improved many patient outcomes including the number of hospitalisations, unscheduled visits to doctors, days off from work and study, and bouts of nocturnal asthma.13
Despite our finding that the planned visits increased provision of asthma action plans, the benefits did not flow through to other measures at 12 months. Nevertheless, there were trends towards more comprehensive management and education, better patient understanding of asthma, improved quality of life and fewer asthma symptoms.
One explanation for the lack of sustainability could relate to the current structure of Australian general practice. A Finnish model of care achieved a reduction in the burden of asthma through a focus on GP and patient education, but was highly reliant on asthma nurses.14 Australian GPs do not currently have sufficient consultation time to provide a “complete package” of asthma care. Without a sustainable mechanism for funding nurses to help with educating patients about self-management and with case management, such models are unlikely to have a great impact.15 A method of funding practices that encourages broader infrastructure change, the development of a team culture and workforce innovation may be more effective.16,17
A second explanation could relate to the characteristics of the patients who attended. A discussion of the challenges for asthma management in a previous report includes focusing on difficult patients and recognising asthma as a long-term condition.18 While many patients in our study were willing to respond to a prompt for review, there was still resistance to visiting the GP. This may relate to denial about their condition, their perceptions of their asthma severity (only 37% self-rated this as moderate or severe), or poor perceptions of their level of control (64% rated control as good or very good). The relatively high levels of nocturnal asthma and exacerbations reported suggest that many did not have well controlled asthma. Mismatches between perception and objective assessment have previously been identified as barriers to attending doctors for review and to optimal self-management behaviour, compounded by a common view of asthma as an episodic condition.19,20 It is possible that if this model had targeted newly diagnosed, uncontrolled or non-compliant patients, it may have produced improvements in health outcomes. Cost of the visit was not seen as a deterrent, as the majority of practices bulk-billed.
Limitations of our study include our failure to reach the desired sample size; this may have reduced the power to detect differences. Also, the demographic characteristics of our patients did not fully represent those of the sampling frame, so our results may not be generalisable.
Because this was a pragmatic trial, eligibility was based on GP diagnosis of moderate or severe asthma. Even though patient report and spirometry testing cast some doubt on the diagnosis and/or severity of asthma in a few cases, we accepted the GP diagnosis. However, if some patients had only mild asthma, or they were already well controlled, there may have been little room for improvement from the intervention.
The failure to successfully implement the model of systematic asthma care we trialled in Australia calls into question whether a practice-based focus on proactive review for every patient with moderate or severe asthma is currently feasible. A previously described chronic illness model suggests that, as well as changes to the organisation of planned care similar to those carried out in our project, improving the quality of care in general practice requires broader workforce reform and changes to community awareness, self-management support and decision support.21
1 Recruitment of practices and patients, and patient retention throughout the trial
 |
|
* Including partial case-note data for four patients in each arm who withdrew. |
2 Characteristics of patients in the control and intervention groups at baseline and comparison with non-participating patients
Characteristic |
Control |
Intervention |
Total participants |
Non-participants |
|||||||||||
Total number |
295 |
270 |
565 |
5368 |
|||||||||||
Mean age in years (range) |
57.6 (18–84) |
58.4 (18–89) |
58.0 (18–89) |
49.3 (18–98) |
|||||||||||
Male |
112 (38.0%) |
94 (34.8%) |
206 (36.5%) |
2159 (40.2%) |
|||||||||||
Socioeconomic index, based on postcode |
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
Low or low–medium |
165 (56.0%) |
181 (67.1%) |
346 (61.2%) |
2537 (47.3%) |
|||||||||||
Medium–high or high |
129 (43.7%) |
89 (33.0%) |
218 (38.6%) |
2815 (52.4%) |
|||||||||||
Missing data |
1 (0.3%) |
0 |
1 (0.2%) |
16 (0.3%) |
|||||||||||
Educational qualifications |
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
High school only |
160 (54.2%) |
143 (53.0%) |
303 (53.6%) |
na |
|||||||||||
Trade, or postsecondary certificate |
53 (18.0%) |
57 (21.1%) |
110 (19.5%) |
|
|||||||||||
Diploma, degree or higher |
82 (27.8%) |
70 (25.9%) |
152 (26.9%) |
|
|||||||||||
Employment status |
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
Employed |
117 (39.7%) |
88 (32.6%) |
205 (36.2%) |
na |
|||||||||||
Retired |
117 (39.7%) |
133 (49.3%) |
250 (44.3%) |
|
|||||||||||
Home duties or other |
61 (20.6%) |
49 (18.1%) |
110 (19.5%) |
|
|||||||||||
Smoking status |
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
Current smoker |
25 (8.5%) |
22 (8.1%) |
47 (8.3%) |
na |
|||||||||||
Ex-smoker |
125 (42.4%) |
103 (38.1%) |
228 (40.3%) |
|
|||||||||||
Never smoked |
144 (48.8%) |
145 (53.7%) |
289 (51.2%) |
|
|||||||||||
Missing data |
1 (0.3%) |
0 |
1 (0.2%) |
|
|||||||||||
Self-rating of asthma severity |
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
Not a problem or mild |
182 (61.7%) |
171 (63.3%) |
353 (62.5%) |
na |
|||||||||||
Moderate or severe |
113 (38.3%) |
98 (36.3%) |
211 (37.3%) |
|
|||||||||||
Missing data |
0 |
1 (0.4%) |
1 (0.2%) |
|
|||||||||||
Self-rating of asthma control |
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
Very good or good |
188 (63.7%) |
172 (63.7%) |
360 (63.7%) |
na |
|||||||||||
Satisfactory |
86 (29.2%) |
83 (30.7%) |
169 (29.9%) |
|
|||||||||||
Poor or very poor |
21 (7.1%) |
15 (5.6%) |
36 (6.4%) |
|
|||||||||||
na = not applicable. |
|||||||||||||||
3 Comparison of clinical outcomes at 12 months for the control and intervention group patients*†
Measure |
Control group |
Intervention group |
Rate ratio (RR) or mean difference (MD) (95% CI) |
||||||||||||
No. with data† |
% Affected or mean volume |
No. with data† |
% Affected or mean volume |
||||||||||||
Asthma on waking at least weekly in previous 4 weeks‡ |
226 |
28.8% |
207 |
31.7% |
RR, 1.1 (0.8 to 1.4) |
||||||||||
Nocturnal asthma at least weekly in previous 4 weeks |
226 |
29.2% |
208 |
20.7% |
RR, 0.7 (0.5 to 1.0) |
||||||||||
At least 1 day off work in previous 4 weeks |
209 |
22.5% |
197 |
30.0% |
RR, 1.3 (1.0 to 1.8) |
||||||||||
Any emergency hospital visit in previous 6 months |
227 |
5.7% |
208 |
2.1% |
RR, 0.4 (0.1 to 1.4) |
||||||||||
At least one exacerbation in previous 4 weeks |
227 |
46.2% |
208 |
39.1% |
RR, 0.8 (0.7 to 1.1) |
||||||||||
Postbronchodilator FEV1/FVC ratio > 75% |
202 |
37.1% |
190 |
34.6% |
RR, 0.9 (0.7 to 1.2) |
||||||||||
Mean postbronchodilator FEV1 |
202 |
2.21 L |
190 |
2.13 L |
MD, − 0.08 (− 0.26 to 0.11) |
||||||||||
FEV1 = forced expiratory volume in 1 second. FVC = forced vital capacity. * All figures adjusted for multiple comparisons, clustering and confounders (education, asthma severity, smoking status). † Some patient data are missing for individual variables. ‡ Primary endpoint. |
|||||||||||||||
4 Comparison of process of care measures at 12 months — mean rates per patient over the previous 6 months*
Measure |
Control group (n = 290) |
Intervention group (n = 261) |
Rate ratio (95% CI) |
||||||||||||
Written asthma action plan† |
0.07 |
0.13 |
1.9 (1.0–3.5)‡ |
||||||||||||
Spirometry performed at least 6-monthly |
0.09 |
0.10 |
1.1 (0.7–2.0) |
||||||||||||
Education about trigger factors |
0.02 |
0.04 |
2.6 (1.0–6.5) |
||||||||||||
Education about preventer medications |
0.02 |
0.05 |
3.1 (0.8–11.6) |
||||||||||||
Education about reliever medications |
0.02 |
0.04 |
2.4 (0.6–9.6) |
||||||||||||
Number of planned visits |
0.14 |
0.20 |
1.4 (0.9–2.0) |
||||||||||||
Assessment of asthma control |
0.14 |
0.17 |
1.2 (0.8–1.8) |
||||||||||||
* All figures adjusted for multiple comparisons, clustering and confounders (education, asthma severity, smoking status). † Primary endpoint. ‡ Statistically significant (P = 0.04). |
|||||||||||||||
5 Outcomes on secondary hypothesis measures — acceptability, quality of life and asthma self-management skills at 12 months*
Measure |
Control group |
Intervention group |
Mean difference (95% CI) |
||||||||||||
Acceptability |
|
|
|
||||||||||||
Number of patients |
na |
270 |
|
||||||||||||
Response to postcard prompt |
|
|
|
||||||||||||
Made a review appointment |
na |
123 (45.6%) |
na |
||||||||||||
Attended a review appointment |
na |
87 (32.2%) |
na |
||||||||||||
Number of patients with data |
227 |
208 |
|
||||||||||||
Satisfaction with general practitioner’s management of asthma† |
7.81 |
8.18 |
0.37 (− 0.15 to 0.89) |
||||||||||||
Satisfaction with practice’s management of asthma† |
8.04 |
8.32 |
0.27 (− 0.15 to 0.69) |
||||||||||||
Quality of life |
|
|
|
||||||||||||
Overall mean score‡ |
4.84 |
4.91 |
0.07 (− 0.16 to 0.29) |
||||||||||||
4.65 |
4.80 |
0.15 (− 0.07 to 0.37) |
|||||||||||||
Mean activity scale score |
5.30 |
5.15 |
− 0.15 (− 0.37 to 0.08) |
||||||||||||
Mean emotional scale score |
4.96 |
5.19 |
0.23 (− 0.03 to 0.49) |
||||||||||||
Mean environment scale score |
4.41 |
4.47 |
0.07 (− 0.34 to 0.47) |
||||||||||||
Self-management skills |
|
|
|
||||||||||||
Management of slow-onset attack§ |
9.29 |
10.37 |
1.07 (0.33 to 1.82) |
||||||||||||
Management of rapid-onset attack¶ |
9.07 |
9.20 |
0.13 (− 0.60 to 0.86) |
||||||||||||
Attitudes and beliefs** |
92.68 |
95.08 |
2.40 (0.53 to 4.26) |
||||||||||||
na = not applicable. * All figures adjusted for multiple comparisons, clustering and confounders (education, asthma severity, smoking status). † Mean score of a rating on a 10 cm visual analogue scale. ‡ Mean score on a scale of 0–7. § Mean score, maximum of 25. ¶ Mean score, maximum of 27. ** Mean score, maximum of 124. |
|||||||||||||||
Received 11 August 2009, accepted 17 June 2010
- Christine H Holton1
- Justin J Beilby1
- Mark F Harris2
- Clare E Harper2
- Judith G Proudfoot2
- Emmae N Ramsay1
- Richard E Ruffin1
- 1 University of Adelaide, Adelaide, SA.
- 2 University of New South Wales, Sydney, NSW.
We thank the practices and patients who participated in this study, the research nurses in SA and NSW who undertook data collection, and the staff of the Data Management and Analysis Centre of the University of Adelaide who designed and managed the study database. We are also grateful to Alan Crockett, who provided spirometry training to the research nurses and general advice to the study team, and to statistician Justin Lokhorst, who developed the statistical analysis plan. This study was funded by the Australian Government through a National Health and Medical Research Council Project Grant (299024).
None identified.
- 1. Australian Centre for Asthma Monitoring. Asthma in Australia 2008. AIHW Asthma Series 2. Canberra: AIHW, 2008. (AIHW Cat. No. ACM 14.)
- 2. Australian Government Department of Health and Ageing. General practice in Australia: 2004. Canberra: DoHA, 2005.
- 3. Wooldridge M. $48.4 million for better asthma care [media release]. Canberra: Department of Health and Aged Care, 8 Oct 2001. http://www.health.gov.au/internet/main/publishing.nsf/Content/health-mediarel-yr2001-mw-mw01102.htm (accessed Feb 2010).
- 4. Beilby J, Holton C. Chronic disease management in Australia: evidence and policy mismatch, with asthma as an example. Chronic Illness 2005; 1: 73-80.
- 5. Medicare Australia. Medicare Australia statistics. Medicare item reports. https://www.medicareaustralia.gov.au/statistics/mbs_item.shtml (accessed Feb 2010).
- 6. Glasgow NJ, Ponsonby AL, Yates R, et al. Proactive asthma care in childhood: general practice based randomised controlled trial. BMJ 2003; 327: 659-666.
- 7. National Asthma Council. Asthma management handbook 2002. Melbourne: NAC, 2002.
- 8. Juniper EF, Guyatt GH, Cox FM, et al. Development and validation of the Mini Asthma Quality of Life Questionnaire. Eur Respir J 1999; 14: 32-38.
- 9. Sibbald B, Collier J, D’Souza M. Questionnaire assessment of patients’ attitudes and beliefs about asthma. Fam Pract 1986; 3: 37-40.
- 10. Sibbald B. Patient self care in acute asthma. Thorax 1989; 44: 97-101.
- 11. Kolbe J, Vamos M, James F, et al. Assessment of practical knowledge of self-management of acute asthma. Chest 1996; 109: 86-90.
- 12. Gibson PG, Powell H. Written action plans for asthma: an evidence based review of the key components. Thorax 2004; 59: 94-99.
- 13. Gibson PG, Coughlan J, Wilson AJ, et al. Self-management education and regular practitioner review for adults with asthma. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2003; (1): CD001117.
- 14. Haahtela T, Tuomisto LE, Pietinalho A, et al. A 10 year asthma programme in Finland: major change for the better. Thorax 2006; 61: 663-670.
- 15. Zwar N, Harris M, Griffiths R, et al. A systematic review of chronic disease management. Canberra: Australian Primary Health Care Research Institute, 2006. http://www.anu.edu.au/aphcri/Domain/ChronicDiseaseMgmt/index.php (accessed May 2009).
- 16. Harris MF, Zwar NA. Care of patients with chronic disease: the challenge for general practice. Med J Aust 2007; 187: 104-107. <MJA full text>
- 17. McDonald J, Cumming J, Harris M, et al. Systematic review of comprehensive primary health care models. Canberra: Australian Primary Health Care Research Institute, 2006. http://www.anu.edu.au/aphcri/Domain/PHCModels/index.php (accessed May 2009).
- 18. Partridge MR. Asthma: 1987–2007. What have we achieved and what are the persisting challenges? Prim Care Respir J 2007; 16: 145-148.
- 19. Burgess T, Beilby J, Zwar N, et al. Evaluation of the Asthma 3+ Visit Plan. Final report. Canberra: Australian Government Department of Health and Ageing, 2004.
- 20. Halm EA, Mora P, Leventhal H. No symptoms, no asthma: the acute episodic disease belief is associated with poor self-management among inner-city adults with persistent asthma. Chest 2006; 129: 573-580.
- 21. Bodenheimer T, Wagner E, Grumbach K. Improving care for patients with chronic illness. JAMA 2002; 288: 1775-1779.





Abstract
Objective: To evaluate whether systematic asthma care involving a register-recall system, postcard prompts for review, and education for general practitioners and staff in Australian general practice improves the quality of care and health outcomes for adult patients with moderate to severe asthma.
Design and setting: Cluster randomised controlled trial in 40 general practices in urban and rural South Australia and New South Wales over the 2 years 2004 and 2005; practices were randomly allocated to the intervention or control group.
Participants: 565 adult patients of these randomly allocated practices who had doctor-diagnosed moderate to severe asthma and were taking inhaled corticosteroids.
Main outcome measures: Clinical asthma indicators, quality of care, acceptability of the intervention to patients, quality of life, and asthma self-management skills at baseline, 6 months and 12 months.
Results: Although 46% of patients in the intervention group practices responded to the postcard prompts, only 32% actually attended for their asthma review. At 12 months, there was a statistically significant difference in provision of written asthma action plans (rate ratio, 1.9; 95% CI, 1.0–3.5; P = 0.04) for intervention group patients compared with control group patients; there was no significant difference in other indicators.
Conclusion: We found little objective evidence of improvement in patient management and outcomes resulting from a systematic model of asthma care.
Trial registration: Australian New Zealand Clinical Trials Registry ACTRN12605000091606