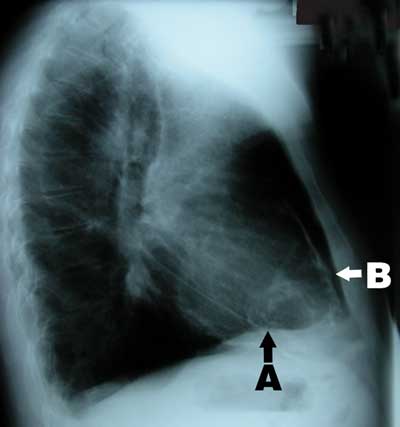
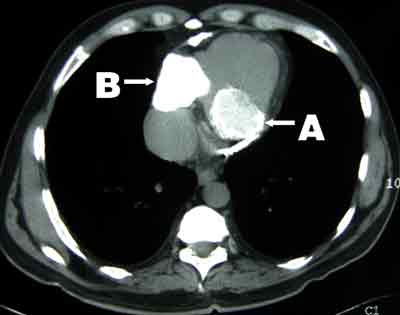
A 58-year-old man of British descent presented in 2003 with chest pain, facial flushing and elevated jugular venous pressure but no leg oedema. He had been exposed to tuberculosis in childhood, had a strongly positive tuberculin test and had been followed up in the tuberculosis surveillance program with regular chest x-rays, but had never been diagnosed with tuberculosis. Chest x-ray on presentation showed calcified plaques and masses in the pericardium and mediastinum (Box 1). Computed tomography revealed extensive calcification of the pericardium (Box 2). Coronary angiography showed 70% stenosis in the left anterior descending artery. Cardiac catheterisation showed equalisation of diastolic pressures in all four chambers, with a positive square root sign (pattern of ventricular diastolic pressure characteristic of constrictive pericarditis).
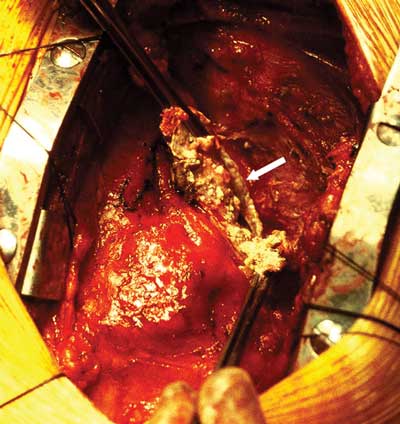
Pericardiectomy with left internal mammary bypass graft to the left anterior descending artery was performed. Severe constrictive pericarditis with a thick (up to 4 mm) layer of calcium plaque was found. Two large cystic masses within a thick calcified shell were present in the posterolateral aspect of the right side of the heart and the left posterior atrioventricular groove. Both contained creamy caseous material, which was drained (Box 3). Histopathological examination was consistent with chronic calcific pericarditis with no granuloma. Microbiological examination and culture did not show any organisms.
The patient was treated with a 6-month regimen for Mycobacterium tuberculosis based on his known previous exposure to tuberculosis, strongly positive tuberculin test, and the operative and pathological findings. Corticosteroid therapy, which is sometimes recommended in the treatment of tuberculosis,1,2 was not considered as the patient did not have effusive pericarditis or active tuberculosis. At 12-month follow-up, he was fully active, without angina or shortness of breath.
In Australia, the annual incidence of tuberculosis is 5–6 cases per 100 000.3,4 Tuberculous pericarditis is seen in 1%–2% of all cases of pulmonary tuberculosis.5 Extensive tuberculous pericarditis is rare in Anglo–Celtic populations.
- Shiromani Goyal1
- Kang-Teng Lim2
- Cheng-Hon Yap3
- Elizabeth W Ryan4
- Morteza Mohajeri5
- Overseas Fellow in Cardiothoracic Surgery; currently, Monash Medical Centre, Melbourne, VIC
- 1. Mayobi BM, Ntsekhe M, Volmink JA, Commerford PJ. Interventions for treating tuberculous pericarditis. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2002; 4: CD000526.
- 2. American Thoracic Society; Centers for Disease Control and Prevention; Infectious Diseases Society of America. Treatment of tuberculosis. MMWR Recomm Rep 2003; 52 (RR-11): 1-77.
- 3. Oliver G, Harvey B. Tuberculosis notifications in Australia, 1995. Commun Dis Intell 1997; 21: 261-269.
- 4. Dawson D. Tuberculosis in Australia: bacteriologically confirmed cases and drug resistance, 1996. Commun Dis Intell 1998; 22: 183-187.
- 5. Larrieu AJ, Tyers GF, Williams EH, Derrick JR. Recent experience with tuberculous pericarditis. Ann Thorac Surg 1980; 29: 464-468.