Prevalence of latex allergy in a dental school
Constance H Katelaris, Richard P Widmer and Ross M Lazarus
Readers may print a single copy for personal use. No further reproduction or distribution of the articles should proceed without the permission of the publisher. For permission, contact the Australasian Medical Publishing Company
Journalists are welcome to write news stories based on what they read here, but should acknowledge their source as "an article published on the Internet by The Medical Journal of Australia <http://www.mja.com.au/>".
Abstract - Introduction - Methods - Results - Discussion - Acknowledgements - References - Authors' details
- ©MJA1997
Abstract |
Objective: To determine the prevalence of latex
allergy in dental workers. Design: Questionnaire survey of staff of a dental school. Setting: The Westmead Dental School, a large dental facility in western Sydney. Participants: 230 staff members of the Westmead Dental School (consisting of general and specialist dentists, chairside assistants and registered nurses, laboratory technicians, dental therapists and hygienists) received questionnaires. Main outcome measures: The prevalence of latex allergy, defined by prompt onset of hand urticaria with or without generalised symptoms, and the prevalence of hand dermatitis and other glove-related symptoms. Also, the relationship between latex allergy and associated atopic status. Results: 177 staff (77%) responded by the set collection date; 33% reported symptoms related to wearing gloves and 22% satisfied the criteria for glove dermatitis. Sixteen respondents (9%) reported characteristics suggestive of latex- glove allergy. Conclusions: Confirmation of the 9% prevalence of latex allergy among dental workers will require further studies incorporating an objective measure of IgE-mediated hypersensitivity. |
Introduction |
Adverse reactions to rubber products have been recognised for many
years, and irritant reactions and cell-mediated hypersensitivity
reactions such as contact dermatitis are well described. The latter
are thought to be caused by one or more low-molecular-weight chemical
compounds added in the rubber-making process.1 It is now recognised that latex allergy is a particular problem for certain "at risk" groups, including health care workers, patients with spina bifida or other spinal cord abnormalities and patients who have had multiple operations. In addition, atopic individuals are more likely to develop IgE antibodies to latex protein with increased exposure.2 The clinical manifestations of type I hypersensitivity reactions to latex protein are wide ranging, from contact urticaria to life-threatening anaphylaxis and death. There is now little doubt that at least some episodes of intraoperative anaphylaxis have occurred because the patient has been sensitised by latex and reacts after mucosal contact with the operating staff's gloves. This has led to some institutions providing latex-free operating suites. No studies of latex allergy in Australia have been published. In this study, we examined the prevalence of latex glove-associated symptoms in the staff of a dental institution. Dental workers are an excellent group for studying the question of latex glove-related symptoms as they may wear gloves for 8-10 hours daily, 4-5 days a week, giving them a much greater degree of exposure to latex than most other health care workers. |
Methods |
All 230 staff of the Westmead Dental School, a large dental facility in
western Sydney, New South Wales, were surveyed by anonymous
questionnaire distributed during Feburary 1995, with a three-week
collection time allocated.
Personnel surveyed included general and specialist dentists, chairside assistants, dental technicians and dental hygienists. |
Questionnaire details |
The questionnaire was divided into four sections.
|
Definitions |
Glove dermatitis: Report of the presence of two or more symptoms of itching, redness and rash (excluding hives) which had been present long term. Latex hypersensitivity: Report of the prompt onset (within 30 minutes of wearing gloves) of hand urticaria with or without the occurrence of allergic rhinoconjunctivitis, lower respiratory tract symptoms such as cough, wheeze or chest tightness, generalised cutaneous itch or urticaria, or upper-airway oedema, hypotension, dizziness or collapse. Atopy: Present if the respondent gave positive answers to any two or more questions on a history of asthma, allergic rhinitis or atopic dermatitis. |
Statistical analysis | All statistical analysis was performed using the SAS package.3 Fisher's exact test was used to test for marginal association in all two-way tables. For other contingency tables, the chi-squared statistic was used to test for marginal association unless otherwise specified. The distribution of demographic characteristics of the staff of the Dental School was used to estimate response rates in order to test for sampling (volunteer) bias. |
Ethical approval | Ethics approval was obtained from the Westmead Hospital Human Research Ethics Committee. |
Results |
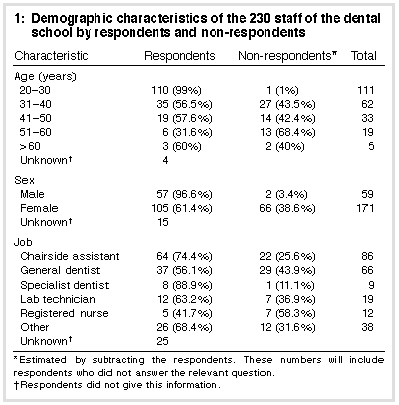
Completed questionnaires were received from 177 of the 230 staff
(77%) by the closing date. Table 1 (below)
shows the distribution of non-response from the population, sampled
by age group, by sex and by job category. Not all respondents answered
all the demographic questions and the response rates are slightly
underestimated because 2.3% of age, 8.5% of sex and 14.1% of job
category data were missing. It was not possible to compare
non-respondents with respondents as the questionnaires contained
no personal identifying data. Year of graduation was the question
most frequently not answered (32 of 177 questionnaires [18%]).
Almost all of the youngest staff responded, whereas among older individuals response rates were as low as 32% for age 51 or 60. As three cells of this Table had expected counts of less than five, we used Fisher's exact test, which showed a significant association (P < 0.00001) between non-response and age group. Men were significantly more likely to respond than women (chi-squared = 26.1; P < 0.00001). The job categories with the highest non-response rates were the small group of registered nurses (58.3%) and the general dentists (43.9%). Evidence that response rate was associated with job category was weak (chi-squared = 11.1; P = 0.05), and this question was not answered by a substantial proportion of respondents. Two-thirds of the study group spent more than half their working day wearing gloves. Symptoms attributed to glove use were reported by one-third of subjects, with itch and redness being the commonest symptoms reported.
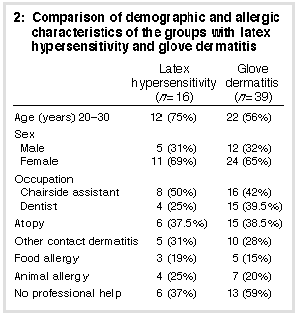
Table 2 (above) compares selected demographic and allergic characteristics of the 39 subjects (22%) who satisfied the criteria for glove dermatitis with the 16 subjects (9%) fulfilling the criteria set for latex hypersensitivity. Other symptomatic and allergic characteristics of the 16 dental workers with latex hypersensitivity are compared with those of the rest of the respondents in Table 3 (below). Almost all of the individuals reporting latex-allergic symptoms also met the criteria for glove dermatitis. Nineteen per cent of the latex-allergic group reported food allergy, although none reported symptoms with foods such as avocado, banana, nuts or soy products, foods which have been described previously as cross-reacting with latex protein. |
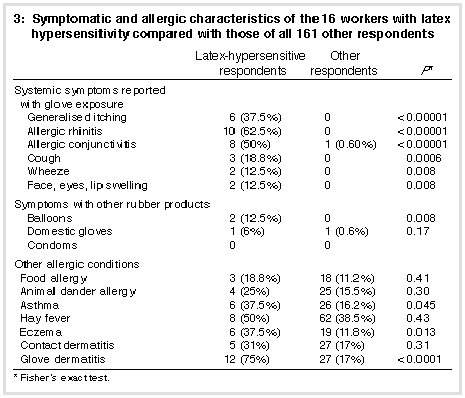 | |
Fisher's exact test was used to test the hypothesis that atopic diathesis was associated with latex hypersensitivity and glove dermatitis. Atopy was associated with both latex hypersensitivity (P = 0.014) and with glove dermatitis (P = 0.006). Subjects who reported experiencing symptoms of either glove dermatitis or latex-allergic symptoms were asked to indicate any action they had taken; of those with glove dermatitis 59% had never sought professional help and one-third of the latex hypersensitivity group had not sought medical attention. | |
Discussion |
Our findings indicate a significant occupational health problem
among dental personnel wearing latex gloves. In our study, 33% of
those surveyed reported some symptoms with glove use; 22% met
criteria for glove dermatitis and 9% for latex allergy.
The distribution of non-response rates by demographic characteristics shown in Table 1 indicates that the volunteer sample was not fully representative of the study population. In particular, female staff, older staff, general dentists and registered nurses were less likely to respond. As a result of these sampling biases, our findings may not be fully generalisable to dental workers. For example, if staff experiencing symptoms were more likely to volunteer for the survey, then our rates will be overestimates of true prevalences. Our results should be interpreted with caution, and future surveys should aim to obtain more representative samples. Relying on questionnaire data alone to determine hypersensitivity reactions has obvious shortcomings. Contact urticaria with glove use may be caused by non-IgE-mediated mechanisms, so our findings may overestimate the prevalence of latex allergy. However, the occurrence of symptoms in other organ systems soon after gloves are used is highly suggestive of an IgE-mediated allergic reaction. Confirmation of this prevalence rate will require some objective measure of IgE-mediated hypersensitivity such as skin testing with appropriate extracts, or in-vitro assay of specific IgE antibodies to the latex allergens. Our prevalence rate of 9% for latex allergy among dental personnel is comparable with, although lower than, rates reported elsewhere. In a similar questionnaire survey without objective testing, Berky et al.4 reported "symptoms of an allergic nature" in 13.7% of 1043 United States Army dental officers. However, this figure included those reporting delayed symptoms as well as those reporting localised contact urticaria or generalised urticarial reactions. Furthermore, a third of those reporting symptoms were unable to be classified as having either contact dermatitis or latex allergy from their questionnaire responses. Only 25% of those reporting latex allergy in the Berky study had consulted a physician. Rankin et al.5 also conducted a questionnaire survey in a large dental facility in the US, obtaining a 15% prevalence of adverse reactions to latex gloves (Table 4). |
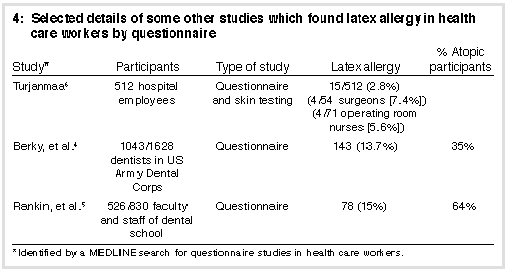 | |
A number of studies4-6 have confirmed a relationship between atopy and latex allergy (Table 4). We also found a significant association when atopy was defined by our criteria (reported presence of any two of asthma, allergic rhinitis or atopic dermatitis). Walsh et al.7 examined factors influencing the wearing of protective gloves in general dental practice in Brisbane. Of 201 dentists who replied to a survey, 84.6% (170) reported that they routinely used gloves in their practice, compared with 13.9% (28) who reported that they did not. Reasons given for not wearing gloves included reduced sensation, reduced movement, low infection risk, skin reaction, patient acceptance and cost. Our results imply that there is a high rate of glove-related symptoms, particularly of glove dermatitis, in this dental workforce. This indicates a need to educate this occupational group about proper hand care as repeated washing, scrubbing and numerous glove changes contribute to hand irritation. Latex allergy has many implications for health care workers which extend beyond the occupational setting. Most reports of life-threatening anaphylactic reactions during surgery and other procedures have involved sensitised health care workers.8 These individuals need to know the risk they run when they themselves are patients. Mucosal contact with latex appears to be a far more potent trigger for anaphylactic reactions than cutaneous contact. People with latex allergy must be given anaesthesia and surgery in a totally latex-free environment. Atopic individuals appear to be especially at risk for sensitisation to the latex protein. Adequate counselling about occupational exposure and advice about methods of minimising the risk need to be considered in view of this and other studies. Latex gloves from different sources vary in the amount of latex protein detectable on the surface.9 Presumably, those with less cause less sensitisation and should be preferred in a workplace where glove use is mandatory. | |
Acknowledgements | We would like to thank Maggie Melink for valuable assistance and the staff of the Westmead Dental School for their cooperation. |
References |
(Received 19 Sep 1995, accepted 6 Apr 1996) |
Authors' details
Department of Immunology, Westmead Hospital, Sydney, NSW.Constance H Katelaris, PhD, FRACP, Senior Consultant.
Department of Paediatric Dentistry, Westmead Dental School,
Sydney, NSW.
Richard P Widmer, MDSc, FRACDS, Associate Professor.
Department of Public Health and Community Medicine, University of
Sydney, Sydney, NSW.
Ross M Lazarus, MB BS, FAFPHM, Lecturer.
Reprints: Dr C H Katelaris, Department of Immunology, Westmead Hospital, Westmead, NSW 2145.
©MJA 1997
<URL: http://www.mja.com.au/> © 1997 Medical Journal of Australia.
Received 4 March 2026, accepted 4 March 2026